-
Home
-
Articles
-
TPE RubberJet Flex: Flexibility and Durability Combined
TPE RubberJet Flex: Flexibility and Durability Combined
Let's explore the unique FLEX material, TPE RubberJet Flex, a thermoplastic elastomer that blends flexibility and durability, making it an excellent choice for a wide range of applications, both in the industrial sector and hobbyist printing. While the material isn't new to our portfolio, its sought-after qualities continue to captivate attention.
Properties of the FLEX Material
TPE RubberJet is based on a blend of polyolefin and SBS blocks, providing exceptional flexibility akin to rubber. This material can absorb vibrations and is highly resistant to pressure, impacts, chemicals, and water. Its matte appearance and non-sticky surface also make it pleasant to touch. It prints exceptionally well and offers numerous possibilities for creating printed objects.
Printing with FLEX and Some Tips from Vojta
When opting to print with FLEX material, there are several important steps to follow. Using adhesive tape for bed adhesion is ideal, and it's crucial to apply the tape with the adhesive side down on a smooth bed surface while reducing the extruder's feed pressure. Excessive pressure can cause filament deformation. The maximum print speed should not exceed 25 mm per second. It's also necessary to slightly raise the initial layer for easier removal of the printed object from the bed.
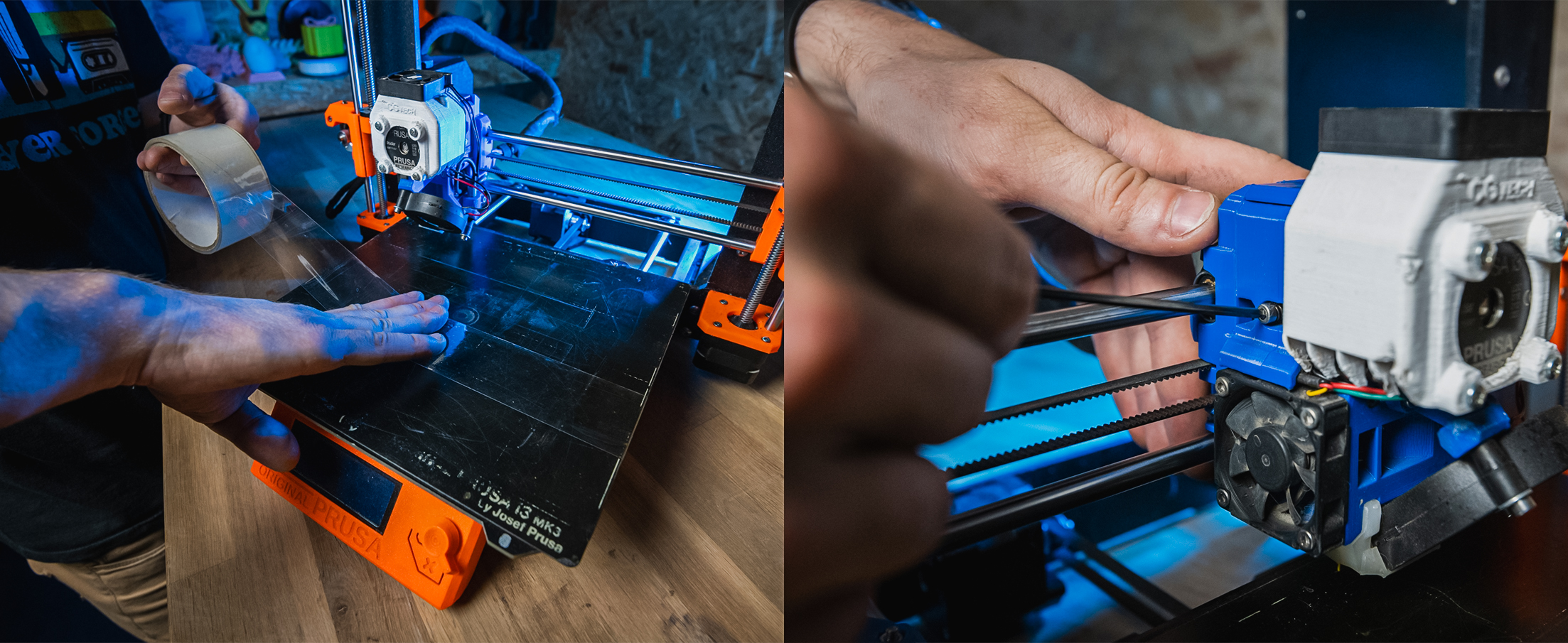
Important: Printing with the heated bed turned off!
When printing with FLEX material, it's key to disable the heated bed. When preparing to remove the finished object, you can heat the bed to 80 degrees Celsius. This approach facilitates the removal of the printed object from the bed.
More than Just a Few Words about FLEX
One of the significant advantages of TPE material is its resistance to humidity, eliminating the need for drying, unlike TPU, for example. The material remains sturdy even at temperatures of up to 100 degrees Celsius, becoming softer as the temperature increases. Its resilience to vibrations and suitability for creating highly impact-resistant objects, such as RC model car wheels, shoe inserts, or seals, are among its strengths.
Differences between TPE88 and TPE32
TPE88 and TPE32 exhibit noticeable differences in hardness. TPE32 represents the harder variant with a Shore hardness value of 32D for its base material. On the other hand, TPE88 offers a softer nature with a Shore hardness value of 88A for its base material. It's important to note that there's a change in hardness during printing. The 100% infill print results in a decrease of approximately 10 Shore hardness units.
.png)
Advantages and Some Drawbacks of FLEX
FLEX offers several benefits, including easy printing, flexibility of printed objects, and excellent vibration dampening. It's resistant to pressure, impacts, chemicals, and water. Layer adhesion is ensured, even when washing printed objects. However, the material may also have its drawbacks, such as weaker bed adhesion (which can be addressed with adhesive tape) and challenges when printing on printers with bowden extruders.
It's worth emphasizing that the challenges when printing with bowden extruders aren't exclusive to our FLEX material. This significant aspect is a common issue faced by anyone working with flexible materials in the market. A bowden extruder requires special attention and adjustments to achieve optimal outputs with these material types.
The FLEX material, TPE RubberJet, brings an excellent combination of flexibility and durability, making it suitable for a wide range of your future projects. Its characteristics and printing possibilities place it at the forefront of interest for many 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Whether you're printing keychains, phone cases, or professional parts that absorb impacts, FLEX material consistently offers reliability and performance.
